Ever experienced a delay or echo during a voice call over the internet? That snag is known as latency, a common gremlin in the world of VoIP communications. VoIP, or Voice over Internet Protocol, has revolutionised how we communicate, seamlessly transforming audio signals into data packets transmitted over the web. But the benefits of VoIP are only as good as the quality it delivers.
Latency is the time it takes for a voice packet to travel from one point to another, and its impact on VoIP is non-trivial. With clear voice quality tantamount to effective communication, latency can mean the difference between a successful conference call or a frustrating game of virtual catch-up. This issue can stem from various factors, such as inadequate bandwidth, network congestion, or outdated hardware—all conspiring to disrupt the seamless flow of conversation.
This article delves into the technical world of VoIP, elucidating the concept of latency, its causes, and the ways to monitor, measure, and mitigate its presence for optimal VoIP performance. Whether you’re a business reliant on VoIP systems, or simply curious about how internet calls work, understanding latency is key to ensuring crisp and clear communication.
Understanding VoIP Communications
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has revolutionised how we communicate by allowing voice to be delivered over the internet. Unlike traditional telephony that relies on circuit-switched networks, VoIP converts voice into digital signal packets, which are then transmitted over IP networks. This technology not only redefines our understanding of a ‘phone call’ but also extends communication capabilities beyond voice, including functionalities such as video conferencing and instant messaging.
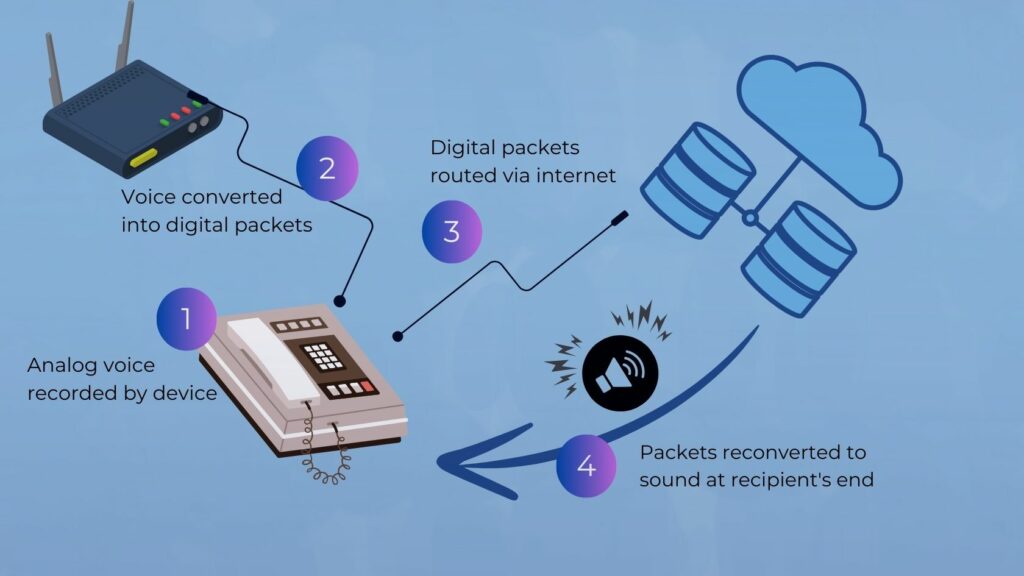
What is VoIP?
VoIP stands for Voice over Internet Protocol, a digital telecommunication technology that permits users to make voice calls using an internet connection instead of a conventional phone line. The technology is an ensemble of methodologies, tasks, and communication protocols that facilitates the delivery of voice communications and multimedia sessions over the internet.
How does VoIP work?
VoIP converts analog voice signals into digital packets of information. These packets travel over the internet or private networks to their destination, where they are reconverted into sound. VoIP systems require an internet service provider and can be accessed using dedicated VoIP phones, computer software, or mobile VoIP apps.
- Encoding: The user’s voice is captured using a microphone and encoded into digital data.
- Packetisation: This digital data is broken into small units called ‘packets’, ready for transmission.
- Routing: Packets are routed through the network to reach their destination.
- Decoding: Once the packets arrive, they are reassembled and decoded back into voice.
Additionally, implementing VoIP encryption is crucial to ensure that these digital packets are secure during transmission, protecting against eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
Advantages of VoIP Communications
VoIP is a giant leap over traditional telephony, bringing forth several key advantages:
Cost-Effectiveness: By using internet networks, VoIP can significantly reduce call costs, especially for long distance and international calls.
Scalability: Adding new users to a VoIP system is typically easier and cheaper than traditional phone systems.
Flexibility: Users can make and receive calls on multiple devices, including phones, laptops, and mobile devices.
Features: VoIP offers extensive features, such as call forwarding, voicemail, and call routing that can all be configured easily through software.
Integration: It integrates well with other business systems, providing a unified communication platform.
VoIP technology is merging the boundaries of communication, offering an efficient and borderless mode of real-time conversation that is increasingly becoming the norm for businesses and individuals worldwide.
The Impact of Latency on VoIP Communications
Latency is often the unseen adversary in Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications, with the potential to substantially impact the quality and clarity of conversations. When engaging in VoIP calls, latency manifests as a noticeable delay between the moment a speaker utters a word and when it reaches the listener’s ear. This delay can disrupt the natural flow of conversation, cause overlap in communication, and lead to frustration among participants. For businesses, high latency levels can undermine the professionalism of a call or video conference, potentially affecting client-perceived credibility. As VoIP relies on real-time transmission of voice packets over the internet, any latency above the acceptable level can tarnish the VoIP experience, making sound quality choppy or causing echoes.

Defining Latency in VoIP Communications
Latency in VoIP communications is measured in milliseconds (ms) and refers to the time interval it takes for a digital voice packet to travel from the source to the destination. The term encompasses all delays incurred during the digital signal processing, packetisation, routing, and buffering of the voice packets across the network. An acceptable latency threshold for VoIP is traditionally considered to be below 150 ms one-way, or 300 ms for round-trip latency, often termed as “two-way latency.” As latency approaches or exceeds this threshold, users begin to notice a degradation in the call’s quality.
Factors Affecting Latency in VoIP Communications
Several factors can influence latency in VoIP communications:
- Internet Connection: The quality and speed of the internet connection play crucial roles. An unstable or slow connection will increase latency.
- Insufficient Bandwidth: A network with insufficient bandwidth can’t handle VoIP traffic effectively, leading to congestion and increased latency.
- Internet Service Provider: The performance of the ISP and the path the packets take through the network can affect latency.
- Outdated Hardware: Older routers, switches, and network infrastructure not optimised for VoIP can introduce unnecessary delays.
- Network Configuration: The Quality of Service (QoS) settings determine network traffic prioritisation. Without proper configuration, voice packets may not be prioritised, resulting in higher latency.
- Distance: The geographical distance between the caller and recipient can affect the number of hops a packet takes to reach its destination, thus impacting latency.
The Importance of Low Latency in VoIP Communications
Achieving low latency is essential for an optimal VoIP experience. Low latency ensures that voice communication is delivered in real time, maintaining the conversational cadence and allowing for natural interactions. This is vital in professional settings where clear, uninterrupted communication is non-negotiable. Low latency is imperative for mission-critical operations like emergency response, trading floors, and remote surgical assistance to ensure decisions and actions are made without detrimental delays. Furthermore, in customer-centric industries, low latency contributes to customer satisfaction, fostering positive engagements and helping to build trust. Therefore, choosing a VoIP provider with a track record of low latency is key, and businesses should continuously monitor their network’s latency levels to preclude any adverse effects on communication quality. Additionally, the use of VoIP adapters can help integrate traditional phone systems with VoIP services, ensuring consistent low-latency performance across various communication devices.
Measuring and Monitoring Latency in VoIP Communications
Keeping a vigilant eye on latency is vital for maintaining the quality of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services. Businesses and VoIP users can gauge latency through various metrics including ‘ping’ test results and through more sophisticated network performance monitoring tools.
Tools for Measuring Latency in VoIP Communications
There is a variety of tools available for measuring VoIP latency:
- Ping Tools: These basic utilities measure round-trip time between the computer and a destination network.
- VoIP-specific Testers: These solutions provide a more comprehensive analysis, evaluating latency, packet loss, and jitter.
- Network Performance Monitors: Advanced systems that allow ongoing tracking, supplying real-time insight into network performance, including latency.
- Quality of Service Monitors: These are often integrated within network hardware to assess VoIP traffic and its performance constantly.
Incorporating these tools can assist in detecting latency issues, providing the necessary data to optimise VoIP performance.
Monitoring Latency Levels for Optimal VoIP Performance
Consistent monitoring is critical for detecting patterns or changes in latency that could signal underlying network issues. Establishing baselines and real-time alerting systems can help network administrators respond quickly to adverse changes. Many VoIP service providers typically offer insight into latency metrics, allowing for timely troubleshooting.
Best Practices for Latency Management in VoIP Communications
To manage latency effectively:
Conduct Regular Testing: Regular latency checks should be part of routine network maintenance.
Prioritise VoIP Traffic: Implement Quality of Service (QoS) rules to prioritise voice packets.
Update Hardware: Ensure that routers and network devices are up-to-date and can handle VoIP traffic efficiently.
Optimise Bandwidth Usage: Monitor bandwidth consumption and limit non-essential uses during high-priority communication times.
Choose a Reliable VoIP Provider: Partner with providers known for their robust infrastructure and low-latency networks.
Network Configuration: Keep the network properly configured for VoIP needs.
By closely measuring and monitoring latency and adhering to these best practices, VoIP users can achieve higher quality communications with minimal disruptions.
Common Causes of Latency in VoIP Communications
Latency in Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) communications can be influenced by various network-related factors that hinder the speed and clarity of voice transmissions. Some of the most common causes of latency include:

Insufficient Bandwidth: When the network doesn’t have enough bandwidth to support VoIP traffic, voice packets are delayed.
Packet Loss: Missing packets can cause interruptions and delays as information needs to be resent or reconstructed.
Internet Service Provider (ISP) Issues: The quality of service from an ISP affects latency levels; a slow or unstable internet connection can result in higher latency.
Network Congestion: High traffic on a network, especially during peak usage times, can slow down VoIP packet delivery.
Inadequate Quality of Service (QoS) Configurations: Without proper QoS settings, VoIP traffic may not be prioritised, leading to increased latency.
Physical Distance: The geographical distance between the caller and the receiver can add to the delay as the digital signal travels further.
Outdated Hardware: Older network equipment may not be optimised for VoIP traffic, causing slower processing speeds.
By understanding these common causes, steps can be taken to mitigate their effects and improve the overall VoIP call quality.
Improving Latency in VoIP Communications
When it comes to Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), latency is a key factor that affects call quality. Latency, often referred to as lag, is the time it takes for a voice packet to travel from the sender to the receiver. High latency can lead to delays and poor communication quality, which is particularly disruptive for real-time conversations. To improve latency in VoIP communications, consider the following actions:
- Conduct regular network assessments to identify and resolve issues that can increase latency.
- Ensure sufficient bandwidth is available to support VoIP needs.
- Prioritise VoIP traffic on your network using Quality of Service (QoS) settings.
- Choose a VoIP service provider known for reliable performance and low latency levels.
- Regularly update and replace outdated network hardware to keep pace with technology.
- Optimise your Wi-Fi network for VoIP traffic, which could include moving closer to the router or using a wired connection.
By implementing these measures, users can significantly reduce latency, and thus, enhance the clarity and efficiency of VoIP calls.
Choosing a Reliable VoIP Service Provider
Selecting the right VoIP service provider is crucial for minimising latency and ensuring high-quality voice communication. When evaluating options, look for providers who offer:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Infrastructure | A robust network optimised for voice traffic with multiple data centers to minimise latency. |
| Quality of Service | Ability to prioritise VoIP traffic over other types of data to reduce lag. |
| Service Level Agreement (SLA) | Clear SLA confirming acceptable latency levels and compensation for not meeting those standards. |
| Customer Support | Access to knowledgeable support teams to help troubleshoot and address latency and other issues. |
| Reputable Performance | A track record of reliability and customer satisfaction, as evidenced by reviews and industry ratings. |
By partnering with a provider that excels in these areas, you can trust that your VoIP calls will be clear and seamless, minimising disruptions due to latency.
Quality of Service (QoS) Measures for Latency Reduction

Quality of Service (QoS) is a set of techniques used to manage network traffic and minimise latency, particularly for real-time applications like VoIP. To effectively implement QoS measures for latency reduction:
Prioritise Voice Traffic: Ensure voice packets are given precedence over other data packets to prevent voice delays.
Bandwidth Reservation: Allocate a portion of your bandwidth exclusively for voice traffic to avoid congestion.
Traffic Shaping: Control the flow of data packets to maintain consistent and reliable VoIP performance.
Policy Enforcement: Create policies that define how different types of traffic are managed on the network.
Upgrading Internet Network Infrastructure for Enhanced VoIP Performance
Upgrading your Internet network infrastructure is vital for achieving the best possible VoIP performance. This initiative goes beyond merely increasing your download speed; it’s about building a robust and reliable foundation that supports real-time communication without lag. Consider the following upgrades:
High-Performance Routers: Upgrade to a router that can handle high speeds and heavy traffic with advanced QoS features.
Reliable ISPs: Choose an Internet Service Provider known for consistent uptime and low latency.
Wired Connections: Use Ethernet cables for devices in fixed locations to provide a more stable connection than Wi-Fi.
Network Cables: Invest in modern network cables, like Cat 6 or higher, that support faster speeds and reduce interference.
Each component in your network contributes to the overall performance and reliability of your VoIP system. Upgrading your infrastructure helps to ensure that voice packets are transmitted smoothly and without delay, providing a professional and high-quality communication experience for users.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Call Quality Affect the Customer Experience?
Call quality is crucial for customer service as it significantly impacts customer experiences. Clear, reliable calls ensure that customers can communicate their needs effectively, reducing frustration and miscommunication. Poor call quality, such as static, echo, or interruptions, can lead to unresolved issues and negative perceptions of the service provided. High-quality calls demonstrate respect for the customer’s time and contribute to a positive first impression and ongoing customer satisfaction.
What is Latency in VoIP Communications?
Latency in VoIP communications refers to the delay between when a voice packet is sent and when it is received. This delay can disrupt the natural flow of conversation, causing overlaps and frustration. It is measured in milliseconds (ms), and an acceptable latency for VoIP is typically below 150 ms one-way.
What Are Common Causes of Latency in VoIP?
Common causes of latency in VoIP communications include:
Insufficient Bandwidth: Not enough bandwidth to support VoIP traffic leads to delays.
Network Congestion: High traffic can slow down packet delivery.
Internet Service Provider (ISP) Issues: Slow or unstable internet connections increase latency.
Outdated Hardware: Older routers and network devices may not handle VoIP efficiently.
Physical Distance: Greater distance between caller and receiver increases latency.
Inadequate QoS Configurations: Without proper Quality of Service settings, voice packets may not be prioritised.
How Can Latency Be Measured and Monitored?
Latency can be measured and monitored using various tools:
Ping Tools: Measure round-trip time between a device and a network.
VoIP-specific Testers: Provide comprehensive analysis including latency, packet loss, and jitter.
Network Performance Monitors: Track real-time network performance and latency metrics.
Quality of Service Monitors: Integrated within network hardware to assess VoIP traffic performance.
What Are the Best Practices to Reduce Latency in VoIP Communications?
Best practices to reduce latency in VoIP communications include:
Regular Network Assessments: Identify and resolve issues that increase latency.
Sufficient Bandwidth: Ensure adequate bandwidth for VoIP needs.
Prioritise VoIP Traffic: Use Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritise voice packets.
Choose Reliable VoIP Providers: Opt for providers with low-latency networks.
Update Hardware: Regularly update or replace outdated network equipment.
Optimise Wi-Fi: Use wired connections where possible and optimise Wi-Fi for VoIP traffic.
How Does Quality Assurance Impact VoIP Call Quality?
Quality Assurance (QA) teams monitor call quality to ensure standards are met, identifying and addressing issues promptly. QA processes include recording and evaluating calls, providing feedback, and implementing improvements. Effective QA ensures high-quality interactions, leading to better customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Why is Low Latency Important for VoIP?
Low latency is essential for maintaining real-time, natural conversations in VoIP communications. High latency disrupts the flow of conversation, causes delays, and can lead to miscommunication. Achieving low latency ensures clear, professional interactions, which are critical for customer service, business operations, and overall user satisfaction.
What is the Role of Quality of Service (QoS) in VoIP?
Quality of Service (QoS) prioritises VoIP traffic over other types of data on a network, reducing latency and improving call quality. Implementing QoS involves configuring network devices to recognise and prioritise voice packets, ensuring that VoIP calls are clear and uninterrupted.
How Can Upgrading Network Infrastructure Enhance VoIP Performance?
Upgrading network infrastructure enhances VoIP performance by ensuring that the network can handle high-speed, high-traffic demands. This includes using high-performance routers, reliable ISPs, wired connections, and modern network cables. Upgraded infrastructure reduces latency, prevents packet loss, and ensures stable, high-quality VoIP calls.
What Should I Look for in a VoIP Service Provider to Minimise Latency?
When choosing a VoIP service provider to minimise latency, look for:
Robust Network Infrastructure: Optimised for low latency.
Quality of Service (QoS): Ability to prioritise VoIP traffic.
Service Level Agreement (SLA): Clear standards for latency.
Customer Support: Responsive and knowledgeable support teams.
Reputation: Positive reviews and industry ratings.
By partnering with a provider that excels in these areas, you can ensure clear and seamless VoIP calls with minimal latency.
Final Words
Latency is a critical factor that can make or break the quality of VoIP communications. By understanding the causes and implementing best practices to measure, monitor, and reduce latency, businesses can ensure clear and professional interactions that enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. From prioritising VoIP traffic with Quality of Service (QoS) settings to upgrading network infrastructure, every step taken towards minimising latency contributes to a seamless communication experience.
VoIP technology has transformed the way we connect, offering flexibility and cost savings. However, its success hinges on maintaining low latency for real-time, natural conversations. By partnering with a reliable VoIP provider and continuously optimising your network, you can provide exceptional communication quality that meets the high standards of today’s digital age.
We’d love to hear your thoughts and experiences with managing latency in VoIP. What strategies have worked best for you? Share your comments below and join the conversation!


