Imagine making a phone call anywhere in the world, anytime, for a fraction of the cost of a traditional landline. Voice over Internet Protocol, or VoIP, turns this into reality, reshaping how we think about communication. Before diving into the depths of VoIP regulation, let’s consider its origins: VoIP services allow voice communications to be made over the Internet, offering an affordable and flexible alternative to classic telephony. As we examine the complexity of regulating such a transformative technology, it’s crucial to understand its advantages and how it differs from conventional phone services.
Navigating the regulatory framework for VoIP services feels like moving through a labyrinth of international and national laws, each with its challenges. From ensuring the safety of users by providing seamless access to emergency services to addressing the unique nature of various VoIP service types, regulators are faced with an evolving task. The ever-changing landscape of VoIP services requires a considered approach, balancing innovation with consumer protection and service quality.
In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the world of consultation documents crafted to refine VoIP regulation, the differentiations among diverse VoIP offerings, and the critical policies to protect users. Whether you are a service provider, consumer, or policy-maker, understanding the intricacies of VoIP regulation is vital in a world increasingly reliant on digital communication. Join us as we peel back the layers of this digital communication revolution and its accompanying regulatory demands.
Overview of VoIP Services
Voice over Internet Protocol, commonly known as VoIP, is transforming the telecommunication landscape by offering innovative ways to manage voice communications over the Internet.

Unlike the age-old traditional telephone networks, VoIP does not rely on dedicated physical lines but takes advantage of internet connectivity’s widespread availability and flexibility.
These services have become prevalent in both business and personal communications, prompting a need for a solid regulatory framework that ensures consumer protection, service quality, and access to critical services such as emergency calls.
Definition and Explanation of VoIP Services
At the heart of its definition, VoIP is a technology that allows voice calls to be made over an internet connection instead of a regular or analogue phone line.
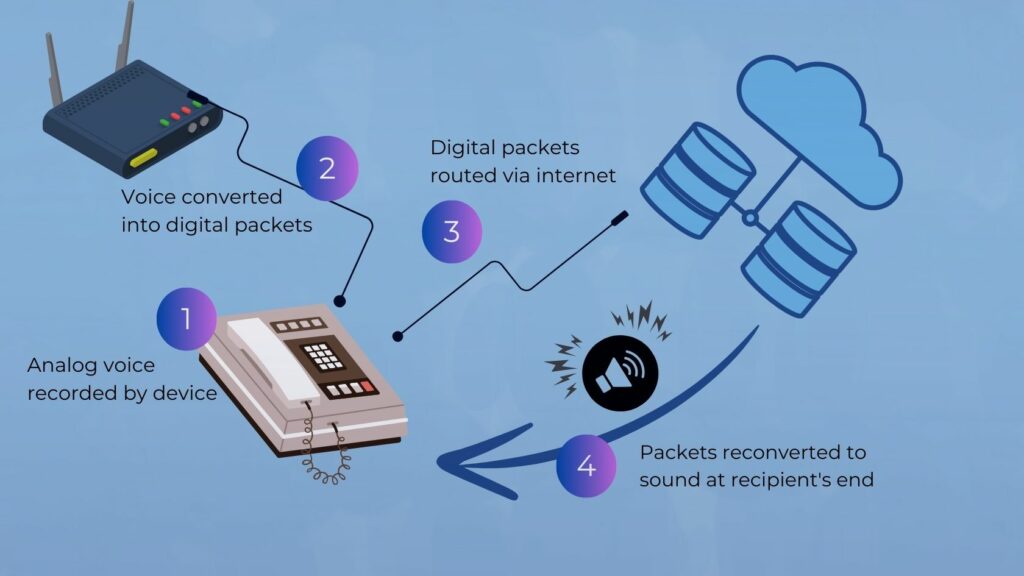
This is achieved by converting voice signals into digital data packets, which travel through private networks or the public internet to the recipient and’re converted back into audio.
There are multiple types of VoIP services, including fixed and nomadic services. Fixed VoIP services are tied to a physical location. At the same time, nomadic VoIP allows users to make and receive calls from any location with internet access, providing mobility and convenience.
Comparison to Traditional Telephone Services
Traditional telephone services, also known as the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), have been the backbone of voice communication for over a century. These systems use circuit switching technology, where a dedicated circuit is established between two points for the duration of a call.

In contrast, VoIP services utilise packet-switched networks, which allow multiple calls to be aggregated over the same infrastructure. This fundamental difference affects deployment, scalability, and costs, where VoIP offers a significant advantage by leveraging existing internet infrastructure.
Benefits and Advantages of VoIP Services
VoIP services offer a range of benefits to consumers and businesses alike. They provide cost-efficiency through reduced call charges, especially for international communication, and they eliminate the need for separate voice and data plans.

VoIP is inherently rich in features, offering functionalities such as call forwarding, voicemail-to-email transcription and video conferencing.
Moreover, its integration with other internet-based services and applications presents an expansive ecosystem of operations, from customer service to collaborative work environments. For consumers, the mobility, flexibility, and advanced features present a compelling case for adopting VoIP over traditional phone services.
Regulatory Framework for VoIP Services
The rise of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services has necessitated the development of a comprehensive regulatory framework to address their unique challenges. Unlike traditional telephony, VoIP operates over the internet, easily crossing geographical and jurisdictional boundaries. As such, a regulatory framework for VoIP services must consider consumer protection, quality of service, competition, interoperability, and security while balancing innovation and flexibility in this rapidly evolving market.

Regulations typically focus on areas such as ensuring that VoIP providers offer access to emergency services, requiring compliance with lawful intercept laws, imposing obligations to contribute to universal service funds, and maintaining customer privacy. They also encompass the obligation of transparency in billing and service changes and address fraud and misuse.
Current Regulatory Landscape
Countries around the world have adopted diverse approaches to regulating VoIP services. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) requires interconnected VoIP providers to comply with requirements similar to those for traditional telephone service providers, including ensuring access to emergency services and contributing to the Telecommunications Relay Services Fund. On the other hand, the European Union’s regulatory approach focuses on a harmonised set of rules to ensure consistent consumer protection and competition within its member states.
Challenges in Regulating VoIP Services
Regulating VoIP services presents several challenges. Firstly, the technological diversity of VoIP services, which can range from peer-to-peer services to fully interconnected ones, makes it difficult to apply a one-size-fits-all regulatory approach. Secondly, the nomadic nature of VoIP complicates the provision of emergency services and the enforcement of geographical-based regulations. Thirdly, contrasting regulatory requirements across jurisdictions can create international compliance complexities for VoIP providers.
In addressing these challenges, regulators must strike a balance between imposing necessary consumer protections and avoiding overregulation that might stifle innovation or create unnecessary burdens.
International and National Regulation of VoIP Services
Regulatory approaches to VoIP services differ significantly worldwide, reflecting national priorities, telecommunications infrastructures, and legal traditions. At the international level, organizations like the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) provide recommendations and standards to guide national regulatory bodies.
In regions such as Europe, the regulatory framework established by the European Electronic Communications Code includes provisions specifically designed to ensure equivalent treatment of VoIP services alongside traditional telecommunication services.
Nationally, regulators have laid out frameworks that range from light-touch oversight to more prescriptive rules. For example, some countries require VoIP providers to ensure their services can connect to emergency services, while others mandate interoperability with the traditional telephone network. Additionally, the integration of SIP Trunking within VoIP services can help meet regulatory requirements by providing a seamless connection between VoIP systems and the traditional public switched telephone network (PSTN), ensuring compliance with emergency service accessibility and interoperability standards.
The primary objectives of these varied regulatory ecosystems remain similar: ensuring fairness in the market, protecting consumers, and fostering an environment where innovative communication technologies can flourish without compromising public welfare or safety.
Regulatory Frameworks for VoIP Services by Country (Table Example)
| Country | Emergency Services Access | Interconnection Obligations | Universal Service Contributions | Lawful Intercept Compliance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory | Mandatory |
| European Union | Harmonised Requirement | Harmonised Requirement | Harmonised Requirement | Harmonised Requirement |
| Japan | Optional | Optional | Optional | Mandatory |
| India | Mandatory | N/A | Mandatory | Mandatory |
Note: The above table is illustrative, not exhaustive or specific to current regulations. Detailed regulations may vary broadly and change over time.
Importance of Emergency Services Access for Voice Calls
Timely access to emergency services through voice calls can mean the difference between life and death. It is essential that all telecommunication services, including VoIP, provide users with the means to reach emergency responders quickly and reliably. Traditional telephone services have long-established mechanisms to connect to emergency numbers, ensuring that distressed individuals can access help wherever they are. For VoIP services, which are becoming increasingly prevalent as a primary mode of communication, the importance of such accessibility is just as critical but inherently more complex due to the technology used.

In scenarios such as medical emergencies, natural disasters, or security incidents, the ability to make a voice call to emergency services is imperative. Voice calls provide immediate two-way communication, which allows dispatchers to assess the situation, provide life-saving instructions, and send the appropriate assistance. The clarity and immediacy of voice calls often make them more effective in emergencies than text messages or other forms of communication.
Consultation Document on Regulation of VoIP Services
Consultation documents serve as a critical tool for gathering input and feedback on proposed changes and challenges related to the regulatory environment of services and industries. They represent an opportunity for stakeholders to play a direct role in shaping policies and regulations that impact the VoIP sector.
Purpose and Scope of the Consultation Document
The purpose of the consultation document on regulating VoIP services is two-fold. Firstly, it exists to outline the proposed regulatory framework intended to oversee VoIP service providers, ensuring they meet certain standards, particularly about access to emergency services. Secondly, the document aims to gather invaluable insights from industry experts, consumers, and other interested parties regarding the proposed regulations’ practicability, impact, and potential improvements.
The scope of this document extends to various aspects of VoIP services, such as consumer protection, technical standards, emergency services access, lawful intercept requirements, and the interconnection with traditional telephone networks. It provides a comprehensive overview of existing regulations and identifies gaps where new rules may be necessary to align with the evolving telecommunications landscape.
Different Types of VoIP Services
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) services have revolutionised the way we communicate, offering various types that cater to different needs. VoIP fundamentally allows voice calls to be made over the Internet, but within this realm, there are multiple service manifestations.
Firstly, Nomadic VoIP Services enable users to make calls from anywhere with internet access. This flexibility allows individuals and businesses to remain connected no matter where they are. However, such benefits come with challenges, particularly in accurately identifying the caller’s location during emergencies.

Peer-to-peer (P2P) VoIP Services, another form, connect users directly without traversing traditional telecommunication networks. This direct connection often means lower costs and the ability to circumvent network congestion. However, this type of VoIP service typically lacks certain functionalities, such as calling regular phone numbers or accessing emergency services.
Interconnected VoIP Services are designed to bridge internet-based calls and the regular telephone network, enabling users to make and receive calls from traditional phone numbers. While this service closely mimics conventional telephone services and includes access to emergency services, it brings about regulatory considerations, particularly in ensuring reliable connections to emergency services and maintaining user privacy.
In deciding on the most suitable type of VoIP service, consumers and businesses must consider factors such as the necessity for traditional phone service interoperability, the need for mobility, cost implications, and potential regulatory requirements.
Nomadic Services: Advantages and Challenges
Nomadic VoIP services stand out for their ability to empower users with mobility — a distinct advantage for a modern, on-the-move society. By not being bound to a specific physical location, these services cater to the influx of remote workers and global nomads who depend on consistent communication access.
However, this very mobility presents notable challenges within the emergency services spectrum. As callers may originate calls from any internet-accessible location, determining the precise geographic location from which a 911 call is made can be complex, potentially slowing down emergency response times. Additionally, these services face difficulty in maintaining service quality across diverse and variable internet connections. They may be less reliable during power outages, requiring specific solutions to ensure continuity of service.
Peer Services: Benefits and Limitations
Peer services, embodying the true decentralised spirit of the internet, offer several distinct advantages. They boast reduced voice call costs and the ability to skirt around network congestion affecting traditional telecom services, ensuring more stable communication under heavy network loads.
Yet, the limitations cannot be overlooked. With peer services, the ability to call traditional landlines or mobile numbers may not exist, limiting communications to within the network of users on the same VoIP service. There is also an absence of access to emergency services, leaving users at potential risk during critical times. Peer services may encounter further limitations in customer service resources, as these platforms may not offer the same level of support as more established telecommunication providers. Additionally, the use of a VoIP virtual numbers might not always be supported by peer services, further restricting the flexibility and reach of communications.
Interconnected VoIP Services: Role and Regulation
Interconnected VoIP services aim to combine the versatility of internet voice calls with the functionality of traditional telephone networks. Users of these services can enjoy the newer technologies of VoIP while still retaining their phone numbers and making and receiving calls from the public switched telephone network (PSTN). This type of service is particularly appealing to businesses that require robust telecommunication capabilities without sacrificing the benefits of VoIP.
The role of regulation in governing interconnected VoIP services becomes paramount to ensure customer welfare and system integrity. Regulatory obligations may encompass mandates for these providers to offer access to emergency services, maintain the confidentiality of communications, and comply with lawful interception requirements. Adaptations may be necessary to ensure these services can effectively and reliably interconnect with the regular telephone network, keeping abreast of consumer expectations and technological advancements.
Given the intricacies of VoIP services, a thorough understanding helps consumers and businesses align their communications needs with the appropriate type of service while staying informed about its benefits, potential drawbacks, and the regulatory obligations that shape its usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP)?
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) is a technology that enables voice communications over the internet rather than traditional phone lines. VoIP converts voice signals into digital data packets, which are transmitted over the internet to the recipient, where they are reassembled into audio signals. This method allows for various communication forms, including voice calls, video conferencing, and messaging, providing a flexible and cost-effective alternative to conventional telephony.
How does VoIP differ from traditional telephone services?
| Feature | Traditional Phone Systems | VoIP |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Method | Physical lines (Copper Wires) | Internet connection |
| Expandability | Limited and costly | Seamless scalability |
| Initial Investment | Higher upfront costs | Lower upfront investment |
| Communication Capabilities | Primarily voice calls | Voice, video, unified communication |
| Flexibility and Mobility | Fixed locations | Accessible anywhere with internet |
| Integration with Other Systems | Limited | High compatibility |
What are the benefits of using VoIP services?
VoIP services offer several benefits, including:
Cost Efficiency: Lower costs for local, long-distance, and international calls.
Scalability: Easily add or remove lines and features without significant infrastructure changes.
Advanced Features: Access to functionalities like call forwarding, voicemail-to-email, video conferencing, and more.
Flexibility: Make and receive calls from any internet-enabled location using various devices.
Integration: Seamless integration with other internet-based services and business applications.
What is the regulatory framework for VoIP services?
The regulatory framework for VoIP services varies by country but typically focuses on consumer protection, quality of service, access to emergency services, lawful intercept compliance, and interoperability with traditional telephone networks. Regulatory bodies aim to balance fostering innovation and ensuring consumer safety and service reliability.
How do different countries regulate VoIP services?
Different countries have varying approaches to regulating VoIP services. For example:
United States: The FCC requires VoIP providers to ensure access to emergency services, contribute to universal service funds, and comply with lawful intercept laws.
European Union: A harmonised regulatory framework ensures consistent consumer protection and competition across member states.
Japan: Regulations may vary, with some requirements being optional.
India: Mandates access to emergency services and compliance with lawful intercept laws.
Why is access to emergency services important for VoIP?
Access to emergency services is critical because it ensures that users can quickly reach emergency responders in times of crisis. VoIP services must provide reliable connections to emergency numbers, despite the technical challenges posed by the technology, such as identifying the caller’s location accurately.
What are the challenges in regulating VoIP services?
Regulating VoIP services involves several challenges:
Technological Diversity: The variety of VoIP services makes a one-size-fits-all regulatory approach difficult.
Nomadic Nature: Users can make calls from any location with internet access, complicating the provision of emergency services.
Jurisdictional Differences: Different countries have varying regulatory requirements, creating compliance complexities for international VoIP providers.
What types of VoIP services are available?
There are several types of VoIP services:
Nomadic VoIP Services: Allow users to make calls from any internet-enabled location.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) VoIP Services: Connect users directly without using traditional telecommunication networks, often lacking emergency service access.
Interconnected VoIP Services: Bridge internet-based calls with traditional telephone networks, enabling calls to and from regular phone numbers and providing access to emergency services.
What are the advantages and challenges of nomadic VoIP services?
Advantages:
Mobility: Users can make calls from anywhere with an internet connection.
Flexibility: Ideal for remote workers and frequent travelers.
Challenges:
Emergency Services: Difficulties in accurately identifying caller locations.
Service Quality: Variable internet connections can affect call quality.
Power Outages: Reliance on internet connectivity can disrupt service during power outages.
How do peer-to-peer VoIP services work?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) VoIP services connect users directly, bypassing traditional telecommunication networks. This method often results in lower costs and reduced network congestion but typically lacks the ability to call regular phone numbers or access emergency services. These services are mainly used within networks of users on the same VoIP platform.
What regulatory obligations do interconnected VoIP services have?
Interconnected VoIP services must comply with several regulatory obligations, including:
Emergency Services Access: Ensuring reliable connections to emergency numbers.
Consumer Protection: Safeguarding user data and ensuring transparent billing practices.
Lawful Intercept Compliance: Enabling lawful interception of communications for security purposes.
Quality of Service Standards: Meeting specified benchmarks for call quality and service reliability.
What are the licensing and registration requirements for VoIP providers?
Licensing and registration requirements for VoIP providers vary by jurisdiction. Some regions require VoIP providers to obtain licenses similar to traditional telecom operators, involving:
Registration with Telecommunications Authorities: To ensure regulatory oversight.
Meeting Technical and Financial Criteria: To ensure service reliability.
Compliance with National Security Considerations: Such as lawful interception capabilities.
How do consumer protection measures apply to VoIP services?
Consumer protection measures for VoIP services typically include:
Transparency in Pricing and Billing: Clear information about service costs and billing practices.
Data Privacy: Protecting customer data from unauthorised access.
Service Limitations: Informing customers about any limitations, such as emergency service access.
Customer Complaints Handling: Mechanisms for addressing customer complaints and disputes.
What Quality of Service (QoS) standards are expected for VoIP providers?
VoIP providers are often required to meet certain QoS standards to ensure reliable and high-quality services, including:
Minimum Connection Speeds: Ensuring adequate bandwidth for clear voice transmission.
Call Quality Parameters: Monitoring latency, jitter, and packet loss to maintain call quality.
Network Availability: Ensuring high uptime and minimal service disruptions.
Disaster Recovery Protocols: Maintaining service continuity during power outages and other disruptions.
What are the benefits of cloud-based VoIP systems?
Cloud-based VoIP systems offer several advantages:
Infrastructure Management: The provider handles infrastructure, reducing the need for on-site hardware.
Flexible Resource Allocation: Dynamically adjusts resources based on demand.
Instant Upgrades and Integrations: Easily add new features and integrate with other systems without physical constraints.
Scalability: Easily scale up or down based on business needs.
How do scalable VoIP systems support business growth?
Scalable VoIP systems support business growth by:
Improving Efficiency: Streamlining communication processes and enhancing staff coordination.
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring responsive service to increasing customer inquiries.
Providing a Competitive Edge: Adapting swiftly to market demands with an agile communication system.
Optimising Resource Allocation: Redirecting funds from communications infrastructure to growth initiatives.
Ensuring Market Responsiveness: Adjusting communication resources without infrastructure lag.
Understanding VoIP services and their regulatory environment is crucial for consumers, businesses, and policymakers. By navigating the complexities of VoIP regulation and leveraging its advantages, stakeholders can ensure robust, reliable, and innovative communication solutions.
Final Words
Imagine making a phone call anywhere in the world, anytime, for a fraction of the cost of a traditional landline. Voice over Internet Protocol, or VoIP, turns this into reality, reshaping how we think about communication. VoIP offers a flexible and affordable alternative to classic telephony, making it an essential tool for modern businesses and individuals alike.
The shift to VoIP is more than just a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic move that can significantly enhance your communication capabilities while reducing costs. Whether you are dealing with the complexities of international calls, the need for scalable communication solutions, or simply looking for advanced features like automated call routing and virtual receptionists, VoIP provides a comprehensive solution.
However, with these advancements come regulatory challenges that must be navigated carefully to ensure consumer protection, service quality, and compliance with emergency services. Understanding the regulatory landscape, from national laws to international guidelines, is crucial for both service providers and users.
Don’t let an outdated phone system hold your business back. Embrace VoIP and experience the benefits of a scalable, cost-effective, and feature-rich communication system. Share your experiences and insights in the comments below. How has VoIP transformed your communication? What challenges have you faced, and how did you overcome them? Your stories and tips can help others make the most of their VoIP journey. Take the first step towards a more efficient and scalable communication system today.

